Mineralized Biofertilizers in Agroecological Systems: Microbial Interactions and Challenges for Production Scaling
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2222Keywords:
sustainable agriculture, biodiversity, soil conservation, agroecological practicesAbstract
The deterioration of agricultural soils, characterized by the progressive reduction in nutrient availability, organic matter, and the loss of soil structure and populations of beneficial microorganisms, represents a critical challenge that threatens
food security due to its adverse ef fects on crop production and the sustainability of agricultural systems. In this context, the implementation of agroecological practices emerges as a key strategy for soil preservation and restoration.
Agroecology, as a discipline, integrates ecological principles to design sustainable food systems that operate in harmony with nature, minimizing dependence on chemical inputs that negatively af fect ecosystems. Among agroecological strategies, the use of mineralized biofertilizers stands out as a promising alternative for restoring the soil microbiome, improving plant nutrition, and promoting environmentally friendly agricultural systems. These biofertilizers contain beneficial microorganisms, such as nitrogen-fixing, cellulose-degrading, and siderophore-producing bacteria, that establish symbiotic interactions with plants and the surrounding soil environment. These interactions contribute to key processes such as nutrient mineralization and solubilization, enhancing the uptake and assimilation of essential macro- and micronutrients by crops.
The objective of this review is to compile and analyze the agroecological potential of mineralized biofertilizers in plant nutrition and the restoration of degraded soils, with emphasis on their production techniques, the beneficial microorganisms involved, and their reported agronomic benefits in various crops. To this end, a bibliographic search was conducted in scientific databases such as Scopus, Web of Science, PubMed, Google Scholar, SciELO, and Redalyc, covering publications in Spanish and English from the last 15 years, with a focus on experimental studies, systematic reviews, and technical and regulatory literature related to agroecological practices and mineral biofertilization.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.
References
Aguado-Santacruz, G.A., Moreno-Gómez, B., Jiménez-Francisco, B., García-Moya, E., & Preciado-Ortiz, R.E. (2012). Impacto de los sideróforos microbianos y fitosideróforos en la asimilación de hierro por las plantas: una síntesis. Revista fitotecnia mexicana, 35(1), 9-21. Recuperado en 01 de septiembre de 2024, de http://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S018773802012000100004&lng=es&tlng=es
Ahemad, M., & Kibret, M. (2014). Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: Current perspective. Journal of King Saud University - Science, 26(1), 1-20. DOI: 10.1016/j.jksus.2013.05.001
Ahmed, B., Zaidi, A., Khan, M. S., Rizvi, A., Saif, S., & Shahid, M. (2017). Perspectives of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in growth enhancement and sustainable production of tomato. In A. Zaidi & M. S. Khan (Eds.), Microbial strategies for vegetable production (pp. 125-149). Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature.
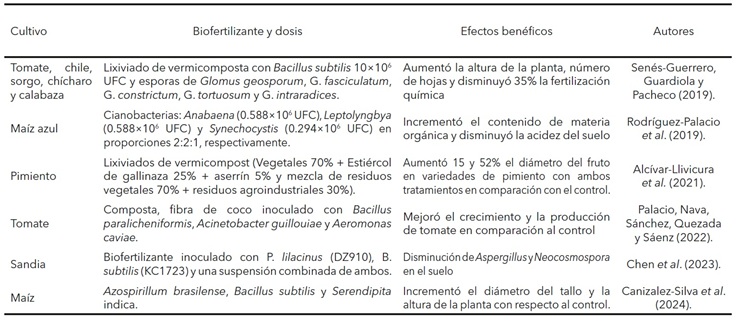
Alcívar LlM, Vera R JH, Arévalo SO, Arévalo SB, Pachar OL, Castillo RC. (2021). Aplicación de lixiviados de vermicompost y respuesta agronómica de dos variedades de pimiento. Rev Colombiana Cienc Anim. Recia. 2021; 13(1):e793. https://doi.org/10.24188/recia.v13.n1.2021.793
Álvarez, C., & Osorio, W. (2014). Silicio agronómicamente esencial. Medellín, Colombia: Universidad Nacional de Colombia.
Araya, M. A., Camacho, M. E., Molina, E., & Cabalceta G. (2015). Evaluación de fertilizantes líquidos con silicio, calcio o magnesio sobre el crecimiento del sorgo en invernadero. Agronomía Costarricense, 39(2), 47-60.
Armenta-Bojórquez, A. D., García-Gutiérrez, C., Camacho-Báez, J. R., Apodaca-Sánchez, M. Á., Gerardo-Montoya, L., & Nava-Pérez, E. (2010). Biofertilizantes en el desarrollo agrícola de méxico. Ra Ximhai, 6(1), 51-56.
Basu, A.; Prasad, P.; Das, S. N; Kalam, S.; Sayyed, R. Z; Reddy, M. S. and Enshasy, H. E. (2021). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) as green bioinoculants: recent developments, constraints, and prospects. Sustainabiliy. 13(3):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ su13031140.
Beltrán Pineda, M. E. (2015). La solubilización de fosfatos como estrategia microbiana para promover el crecimiento vegetal. Ciencia y Tecnología Agropecuaria, 15(1), 101–113. https://doi.org/10.21930/rcta.vol15_num1_art:401
Bybordi A, Saadat S., Zargaripour, P. (2017). The effect of zeolite, selenium and silicon on qualitative and quantitative traits of onion grown under salinity conditions. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science 1: 1-11.
Calvo, P., Nelson, L., & Kloepper, J. W. (2014). Agricultural uses of plant biostimulants. Plant and Soil, 383(1- 2), 3-41. doi: 10.1007/s11104-014-2131-8
Canizalez-Silva, M., Blanco-Macías, F., España-Luna, M. P., de la Rosa-Rodríguez, R., Lara-Herrera, A., & Lozano-Gutiérrez, J. (2024). Microorganismos en la biofertilización del cultivo de maíz como complemento a la fertilización química. Ecosistemas Y Recursos Agropecuarios, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.19136/era.a11n1.3903
Chávez-Díaz, I. F., Zelaya-Molina, L. X., Cruz-Cárdenas, C.I., Rojas-Anaya, E., Ruíz-Ramírez, S., & Santos-Villalobos, S. (2020). Consideraciones sobre el uso de biofertilizantes como alternativa agro-biotecnológica sostenible para la seguridad alimentaria en México. Revista mexicana de ciencias agrícolas, 11(6), 1423-1436. Epub 11 de octubre de 2021.https://doi.org/10.29312/remexca.v11i6.2492.
Chen, T.,Zhang, S.,& Yuan, Z. (2020). Adoption of solid organic waste composting products: A critical review. Journal of cleaner production, 272,1-10.
Chen, P., Zhang, J., Li, M., Fang, F., Hu, J., Sun, Z., Zhang, A., Gao, X., & Li, J. (2023). Synergistic effect of Bacillus subtilis and Paecilomyces lilacinus in alleviating soil degradation and improving watermelon yield. Frontiers in microbiology, 13, 1101975. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1101975
Corrales-Ramírez, L.C., Arévalo-Galvez, Z.Y., & Moreno-Burbano, V.E. (2014 a). Solubilización de fosfatos: una función microbiana importante en el desarrollo vegetal. Nova, 12(21), 68-79.
Corrales-Ramírez, L.C., Caycedo-Lozano, M.A. Gómez-Méndez, S.J., Ramos-Rojas, & J. N. Rodríguez-Torres. (2017 b). Bacillus spp: Una alternativa para la promoción vegetal por dos caminos enzimáticos. NOVA 15: 45-65. doi: https://doi.org/10.22490/24629448.1958
Dehner C.A., Awaya, J.D., Maurice, P.A., DuBois. J.L. (2010). Roles of siderophores, oxalate, and ascorbate in mobilization of iron from hematite by the aerobic bacterium Pseudomonas mendocina. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 76:2041–2048.
Dussi, M.C. & Flores, L.B. (2018). Visión multidimensional de la agroecología como estrategia ante el cambio climático. Inter disciplina, 6(14), 129-153. Epub 15 de febrero de 2021. https://doi.org/10.22201/ceiich.24485705e.2018.14.63384
Etesami, H., S. E & H. A. Alikhani. (2017). Potassium solubilizing bacteria (KSB): Mechanisms, promotion of plant growth, and future prospects - A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 17: 897-911. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162017000400005.
Gao B, Chai X, Huang Y, Wang X, Han Z, Xu X, Wu T, Zhang X, Wang Y. (2022). Siderophore production in pseudomonas SP. strain SP3 enhances iron acquisition in apple rootstock. J Appl Microbiol. Aug;133(2):720-732. doi: 10.1111/jam.15591. Epub 2022 May 9. PMID: 35462451.
González-Fuentes, J.A., Jiménez-López, D., Sandoval-Rangel, A., Hernández-Perez, A., Medrano-Macías, J. & Preciado-Rangel, P. (2020). Efecto de enmiendas minerales sobre el contenido mineral y antioxidantes en frutos de frambuesa. Biotecnia, 22(1), 48-55. Epub 03 de agosto de 2020.https://doi.org/10.18633/biotecnia.v22i1.1124
Goswami, D., Thakker, J. N., Dhandhukia, P. C., & Tejada Moral, M. (2016). Portraying mechanics of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): A review. Cogent Food & Agriculture, 2(1). doi: 10.1080/23311932.2015.1127500.
Gianfreda, L. (2015). Enzymes of importance to rhizosphere processes. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 15(2), 283-306.
Harrington JM, Crumbliss AL. (2009). The redox hypothesis in siderophore-mediated iron uptake. Biometals. Aug;22(4):679-89. doi: 10.1007/s10534-009-9233-4. Epub 2009 Apr 9. PMID: 19357971.
Heredia Hernández, D. & Hernández-Moreno, M.C. (2022). Resistencia a la transición agroecológica en México. Región y sociedad, 34, e1581. Epub 01 de junio de 2023.https://doi.org/10.22198/rys2022/34/1581
Hickman, J. E., Kaya, B., Kebede, A., Kandji, S., Fitch, L., Neill, C. y Palm, C. A. (2021). Little effect of land use on N₂O and NO emission pulses following rewetting of dry soils across seasonally dry sub-Saharan Africa.
Iqbal, A., He, L., Ali, I., Ullah, S., Khan, A., Akhtar, K., Wei, S., Fahad, S., Khan, R., & Jiang, L. (2021). Co-incorporation of Manure and Inorganic Fertilizer Improves Leaf Physiological Traits, Rice Production and Soil Functionality in a Paddy Field. Scientific Reports, 11, 1-16.
Kaur G, Reddy MS. (2013). Influence of P-solubilizing bacteria on crop yield and soil fertility at multilocational sites. European Journal of Soil Biology. 2014;61: 35-40.
Kawaka, F. (2022). Caracterización de bacterias simbióticas y fijadoras de nitrógeno. AMB Expr 12 , 99.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-022-01441-7.
Lazcano, C., Zhu-Barker, X. & Decock, C. (2021). Effects of organic fertilizers on the soil microorganisms responsible for N2O emissions: A review. 9,2-18.
Lebrazi, S., Niehaus, K., Bednarz, H., Fadil, M., Chraibi, M., & Fikri-Benbrahim, K. (2020). Screening and optimization of indole-3-acetic acid production and phosphate solubilization by rhizobacterial strains isolated from Acacia cyanophylla root nodules and their effects on its plant growth. Journal, genetic engineering & biotechnology, 18(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-020-00090-2
Martínez-Aguilar, F. B., Guevara-Hernández, F., Aguilar-Jiménez, C. E., Rodríguez-Larramendi, L. A., Reyes-Sosa, M. B., & La O-Arias, M. A. (2020). Caracterización físico-química y biológica del suelo cultivado con maíz en sistemas convencional, agroecológico y mixto en la Frailesca, Chiapas. REVISTA TERRA LATINOAMERICANA, 38(4), 871–881. https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v38i4.793.
Martínez-Dalmau, J., Berbel, J. y Ordóñez-Fernández, R. (2021). Nitrogen fertilization: A review of the risks associated with the Inefficiency of its use and policy responses. Sustainability, 13: 5625.
Mejía-Carranza, J., Cruz-Chávez, D., Alvarado Hernández, R. & Ramírez Gerardo, M.G. (2022). Aplicación de un compost con aporte de silicio en cultivo de rosa (Rosa x hybrida). Ecosistemas y recursos agropecuarios, 9(3), e3227. Epub 21 de agosto de 2023.https://doi.org/10.19136/era.a9n3.3227
Méndez-Argüello, B., & Lira-Saldivar, R. H. (2019). Uso potencial de la zeolita en la agricultura sustentable de la nueva revolución verde. Ecosistemas y recursos agropecuarios, 6(17), 191-193. Epub 00 de mayo de 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.19136/era.a6n17.1810.
Molina, R. D., Bustillos, C. M. d. R., Rodríguez, A. O., Morales, G. Y. E., Santiago, S. Y., Castañeda, L. M., & Muñoz, R. J. (2015). Mecanismos de fitoestimulación por rizobacterias, aislamientos en América y potencial biotecnológico. Revista de la DES Ciencias Biológicas Agropecuarias, 17(2), 24-34.
Nabti E., Bensidhoum L., Tabli N., Dahel D., Weiss A., Rothballer M., Schmid M., Hartmann A. (2014). Estimulación del crecimiento de la cebada y efecto de biocontrol sobre hongos fitopatógenos por una cepa de Cellulosimicrobium sp. aislada de suelo rizosfera afectado por sal en el noroeste de Argelia. Eur J Soil Biol 2014; 61: 20–6.10.1016/j.ejsobi.2013.12.008.
Noumavo, A. P., Agbodjato, N. A., Baba-Moussa, F., Adjanohoun, A., & Baba-Moussa, L. (2016). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: beneficial effects for healthy and sustainable agriculture. African Journal of Biotechnology, 15(27), 1452-1463. doi: 10.5897/ajb2016.15397.
Olle, M. (2021). Bokashi technology is a promising technology for Crop production in Europe. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology, 96,145-152.
Palacio-Rodríguez, R., Nava-Reyes, B., Sánchez-Galván, H., Quezada-Rivera, J.J, & Sáenz-Mata, J. (2022). Efecto de la inoculación de rizobacterias promotoras del crecimiento vegetal de tomate en condiciones de casa sombra comercial. Revista mexicana de ciencias agrícolas, 13(spe28), 231-242. Epub 13 de enero de 2023.https://doi.org/10.29312/remexca.v13i28.3278
Peñafiel, W.,& Ticona, D. (2015). Elementos Nutricionales en la Producción De Fertilizante Biol con Diferentes Tipos de Insumos y Cantidades de Contenido Ruminal De Bovino-Matadero Municipal de La Paz. Revista de Investigación e Innovación Agropecuaria y de Recursos Naturales, 2,87-90.
Puja H, Mislin GLA, Rigouin C. (2023). Engineering siderophore biosynthesis and regulation pathways to increase diversity and availability. biomolecules. 7;13(6):959. DOI: 10.3390/biom13060959. PMID: 37371539; PMCID: PMC10296737.
Restrepo Rivera, Jairo, . El ABC de la agricultura orgánica y harina de rocas 2007. 1a ed. Managua: SIMAS, 2007 262 p ISBN: 978-99924-55-27-2.
Restrepo-Franco, G.M., Marulanda-Moreno, S., Pérez, Y., Díaz -de la Osa, A., Baldani-Vera, L., Hernández-Rodríguez, A. (2015). Bacterias solubilizadoras de fosfato y sus potencialidades de uso en la promoción del crecimiento de cultivos de importancia económica Revista CENIC. Ciencias Biológicas, vol. 46, núm. 1, enero-abril, 2015, pp. 63-76 Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas Ciudad de La Habana, Cuba
Richardson, A; Simpson, R. (2011). Soil microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability. plant physiology 156:989-996.
Rodríguez, G., Pradenas, H., Basso, C., Barrios, M., León, R., & Pérez, M. (2020). Effect of doses of nitrogen in the agronomy and physiology of yellow passion fruit. Agronomía Mesoamericana Universidad de Costa Rica, 117-128.
Rodríguez-Hernández, M. G., Gallegos-Robles, L., Rodríguez- Sifuentes, M., Fortis-Hernández, J. G., Luna-Ortega Y., & González-Salas, U. (2020). Cepas nativas de Bacillus spp. como una alternativa sostenible en el rendimiento de forraje de maíz. Terra Latinoamericana 38: 313-321. doi: https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v38i2.690.
Rodríguez-Palacio, M., Hernández-Reyes, B., Castilla-Hernández, P., Sánchez-Robles, J., Vela-Correa, G., & Schettino-Bermúdez, B. (2019). Uso potencial de cianobacterias como biofertilizante para el cultivo de maíz azul en la Ciudad de México. Revista Latinoamericana De Biotecnologia Ambiental y Algal, 10(1), 27.
Romero-Arias, A., Ruz-Reyes, R. M., Nápoles-García, M. C., Gómez-Padilla, E. J., & Rodríguez-Rodríguez, S. (2019). Efecto de la aplicación de tres cepas de Bradyrhizobium en el desarrollo morfoagronómico de Glycine max L. Pastos y Forrajes, 42(4), 290-295.
Sarandón, S. J. (2020). Biodiversidad, agroecología y agricultura sustentable. La Plata, Universidad Nacional de La Plata-EDULP.
Senés-Guerrero, C., Guardiola-Márquez, C., & Pacheco-Moscoa, A. (2019). Evaluación de biofertilizantes a base de microorganismos y lixiviado de vermicomposta en cultivos de interés económico en México. Agro Productividad, 12(3). https://doi.org/10.32854/agrop.v0i0.1348.
Souza Rd, Ambrosini A, Passaglia LM. (2015). Plant growth-promoting bacteria as inoculants in agricultural soils. Genet Mol Biol. 2015 Dec;38(4):401-19. DOI: 10.1590/S1415-475738420150053. Epub 2015 Nov 3. PMID: 26537605; PMCID: PMC4763327.
Schwertmann, U.; Taylor, R.M. (1989). Iron oxides in mineral in soil environments (2 Edition) (J. B. Dixon; S. B. Weed eds) Soil Science Society of America. 677 South Segoe Road. Madison. WI 53711. USA.SSA Book Series N°. 1:379-438.
Tabassum, B., Khan, A., Tariq, M., Ramzan, M., Iqbal Khan, M. S., Shahid, N., & Aaliya, K. (2017). Bottlenecks in commercialisation and future prospects of PGPR. Applied Soil Ecology, 121, 102-117. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.09.030.
Tortora M L, J C Díaz–Ricci, R O Pedraza. (2011). Azospirillum brasilense siderophores with antifungal activity against Colletotrichum acutatum. Arch. Microbiol. 193:275–286.
Velasco-Jiménez, Antonio, Castellanos-Hernández, Osvaldo, Acevedo-Hernández, Gustavo, Aarland, Rayn Clarenc, & Rodríguez-Sahagún, Araceli. (2020). Bacterias rizosféricas con beneficios potenciales en la agricultura. Terra Latinoamericana, 38(2), 333-345. Epub 20 de junio de 2020.https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v38i2.470
West, P.C., Gerber, J.S., Engstrom, P.M., Mueller, N. D., Brauman, K. A., Carlson, K. M. y Siebert, S. (2014). Leverage points for improving global food security and the environment. Science, 345(6194): 325-328.
Wu, L., Jiang, Y., Zhao, F., He, X., Liu, H. y Yu, K. (2020). Increased organic fertilizer application and reduced chemical fertilizer application affect the soil properties and bacterial communities of grape rhizosphere soil. Scientific Reports, 10(1): 1-10.
Zhang, X., Guo, J., Vogt, R. D., Mulder, J., Wang, Y., Qian, C., Wang, J., Qian, C. y Wang, J. (2020). Soil acidification as an additional driver to organic carbon accumulation in major Chinese croplands. Geoderma. 366: 114234.