Influence of Three Design Factors and Seasonality on the Removal of Three Drugs by Treatment Wetlands
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2214Keywords:
water pollution, alternative technologies, xenobioticsAbstract
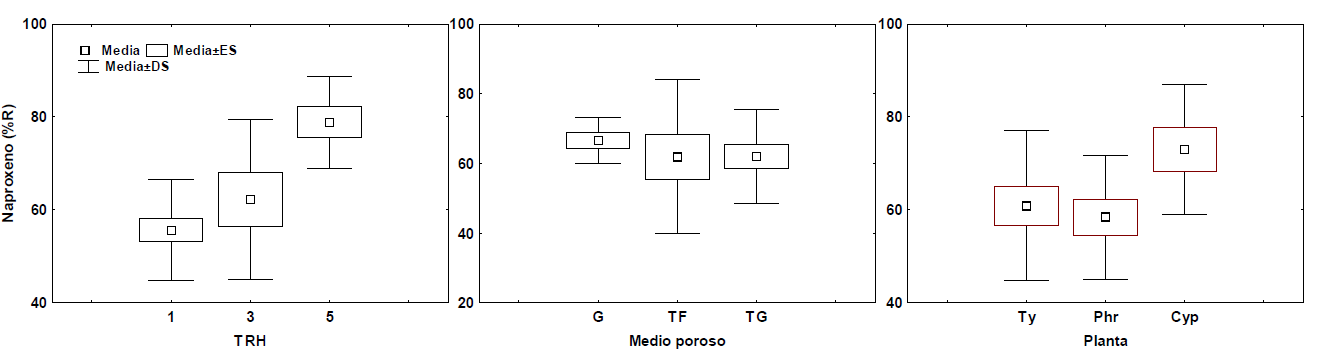
Wastewater use in agriculture represents a global problem because of the presence of many organic micropollutants, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These substances have been reported to harm plant development and other biological processes in crops. Therefore, the objective of the present study is to evaluate the ef fect of three design factors and seasonality on removal ef ficiency of three drugs by wetlands treatments. Fif teen systems designed according to Latin square were constructed using the following input variables: plant type (Pl), hydraulic retention time (HRT), and type of porous medium (PM), and the output variables were the removal ef ficiencies of naproxen, ibuprofen, and diclofenac to evaluate the ef fect of seasonality. Fif teen samples were grouped into three time periods, and the removal ef ficiencies were statistically compared. The maximum removal percentages of 85.3, 79.0, and 81.8% were obtained for naproxen, ibuprofen, and diclofenac, respectively. Regarding the design factors, only HRT showed a significant ef fect on naproxen removal; however, neither MP nor Pl showed statistically significant variation. In the case of seasonality, better system performance was observed during the warmer period. Only HRT had a significant ef fect on removal ef ficiency, achieving ef ficiencies higher than 50%, which positions these systems as ef fective alternatives for removing these compounds.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.