Biochar from sugarcane apices as a soil conditioner for greenhouse cultivation of Ocimum basilicum var. thyrsiflora
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v40i0.1077Keywords:
Thai basil, biomass, crop nutrition, aromatic plant, organic residuesAbstract
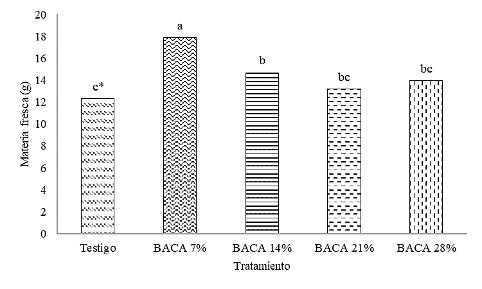
The incorporation of biochar obtained from husks, stubble, forest residues, manures, among other residues into the soil can improve the growth of crops. The objective of our study was to evaluate the effect of sugarcane apice biochar (SAB) on the growth of thai basil (Ocimum basilicum var. thyrsiflora) grown in a greenhouse. The treatments consisted of mixtures of biochar and sandy loam soil (v/v) at 0 (control), 7, 14, 21 and 28% concentrations. Plant height, fresh and dry matter, foliar area, SPAD units and the foliar nutrient concentration were evaluated. The use of 7% SAB increased the fresh matter (45.1%), dry matter (35.2%) and foliar area (54.5%). On the other hand, the 21% SAB treatment showed the highest foliar concentration of total-N (44.33 g kg-1), P (9.55 g kg‑1) and Ca (12.61 g kg-1). We conclude that sugarcane apice biochar can be incorporated into the soil as an alternative in the agronomic management of Thai basil.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.