Emerging Contaminants from Sewage Sludge Application in Agriculture: Bibliometric Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2220Keywords:
bioaccumulation, biosolid, bibliometric indicators, scientific production, VOSviewerAbstract
The production of biosolids in wastewater treatment plants represents an environmental concern, as it increases in parallel with population growth. The literature reports research addressing the application of sludge in agriculture, raising concern about the ef fects of emerging contaminants (EC) that may be present in crops and soils. The aim of this study was to analyze, using bibliometric tools, trends in scientific production related to research on the application of sewage sludge in agriculture during the period from 1992 to 2024. An advanced search was
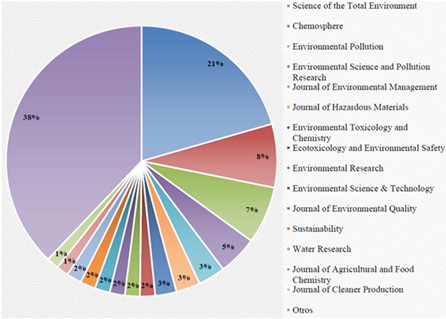
conducted in Web of Science, specifically in the Science Citation Index Expanded and Social Science Citation Index databases, and an analysis of bibliometric indicators was performed in Excel and VOSviewer. A total of 277 registered papers published during the period under study (1992–2024) were obtained. Scientific production followed an exponential growth pattern (R² = 0.9124), indicating an increase in the number of articles published in these years of less than 2% from 1992 to 2011, followed by growth greater than 2%, in contrast to 2021, when the increase exceeded 10%. The author with the highest number of registered publications was Lapen D. R., while the most cited author was Huerta E. The journal with the most published articles was Science of the Total Environment, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences was the institution with the greatest number of registered publications and the highest level of collaboration with institutions in other countries. It is concluded that the growth of literature related to the application of sewage sludge to agricultural fields and its implications concerning EC has been exponential, and that numerous authors are actively publishing in this field of study.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.
References
Abril, C., Santos, J. L., Martín, J., Aparicio, I., & Alonso, E. (2021). Uptake and translocation of multiresidue industrial and household contaminants in radish grown under controlled conditions. Chemosphere, 268, 128823. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128823
Brown, S., Ippolito, J. A., Hundal, L. S., & Basta, N. T. (2020). Municipal biosolids—A resource for sustainable communities. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 14, 56-62. doi:10.1016/j.coesh.2020.02.007
Buta, M., Hubeny, J., Zieliński, W., Harnisz, M., & Korzeniewska, E. (2021). Sewage sludge in agriculture – the effects of selected chemical pollutants and emerging genetic resistance determinants on the quality of soil and crops – a review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 214, 112070. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112070
Clarke, B. O., & Smith, S. R. (2011). Review of 'emerging' organic contaminants in biosolids and assessment of international research priorities for the agricultural use of biosolids. Environment international, 37(1), 226–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2010.06.004
Clarke, B.O., Smith, S.R. (2018). Review of ‘emerging’ organic contaminants in biosolids and assessment of international research priorities for the agricultural use of biosolids. Environ. Int., 37, 226-247, 10.1016/j.envint.2010.06.004
Corradini, F., Meza, P., Eguiluz, R., Casado, F., Huerta-Lwanga, E., & Geissen, V. (2019). Evidence of Microplastic Accumulation in Agricultural Soils from Sewage Sludge Disposal. Sci. Total Environ., 671, 411– 420, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.368
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285-296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Fromme, H., Küchler, T., Otto, T., Pilz, K., Müller, J., & Wenzel, A. (2002). Occurrence of phthalates and bisphenol A and F in the environment. Water research, 36(6), 1429-1438. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00367-0
Gao, D., Li, X. Y., & Liu, H. T. (2020). Source, occurrence, migration and potential environmental risk of microplastics in sewage sludge and during sludge amendment to soil. Science of the Total Environment, 742, 140355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140355
Gubišová, M., Horník, M., Hrčková, K., Gubiš, J., Jakubcová, A., Hudcovicová, M., & Ondreičková, K. (2020). Sewage Sludge as a Soil Amendment for Growing Biomass Plant Arundo donax L. Agronomy, 10(5), 678. doi:10.3390/agronomy10050678
Jones V., Gardner M., & Ellor B. (2014). Concentrations of trace substances in sewage sludge from 28 wastewater treatment works in the UK Chemosphere, 111, 478-484
Hirsch, J. E. (2005). An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences, 102(46), 16569-16572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507655102
Lamastra, L., Suciu, N. A., & Trevisan, M. (2018). Sewage sludge for sustainable agriculture: contaminants’ contents and potential use as fertilizer. Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture, 5(1), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-018-0122-3
Li, J., Wang, Y., & Yan, B. (2018). The hotspots of life cycle assessment for bioenergy: A review by social network analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 625, 1301-1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.030
Li, Z., & Yuan, D. (2024). Global performance and trends of research on emerging contaminants in sewage sludge: A Bibliometric Analysis from 1990 to 2023. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 281, 116597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116597
Marchuk, S., Tait, S., Sinha, P., Harris, P., Antille, D. L., & McCabe, B. K. (2023). Biosolids-derived fertilisers: A review of challenges and opportunities. Science of the Total Environment, 875, 162555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162555
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & Prisma Group. (2010). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. International Journal of Surgery (london, England), 8(5), 336–341.
Niknejad, N., Ismail, W., Bahari M., Hendradi, R., & Salleh, A. Z. (2021) ‘Mapping the research trends on blockchain technology in food and agriculture industry: a bibliometric analysis’, Environ. Technol. Innovat., 21, doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2020.101272
Pérez-Lemus, N., López-Serna, R., Pérez-Elvira, S. I., & Barrado, E. (2019). Analytical methodologies for the determination of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in sewage sludge: A critical review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1083, 19-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.06.044
Pérez, R. A., Sánchez-Brunete, C., Albero, B., Miguel, E., Tadeo, J. L., Alonso, J., & Lobo, M. C. (2016). Quality assessment of three industry-derived organic amendments for agricultural use. Compost Science & Utilization, 24(3), 190-202. https://doi.org/10.1080/1065657X.2015.1124817
Sorinolu, A. J., Tyagi, N., Kumar, A., & Munir M. (2021). Antibiotic resistance development and human health risks during wastewater reuse and biosolids application in agriculture, Chemosphere, 265, 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129032
Seleiman, M. F., Santanen, A., & Mäkelä, P. S. (2020). Recycling sludge on cropland as fertilizer–Advantages and risks. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 155, 104647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104647
Shoaib, M., Zhang, S., & Ali, H. (2023). A bibliometric study on blockchain-based supply chain: a theme analysis, adopted methodologies, and future research agenda. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(6), 14029-14049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24844-2
Shu, W., Price, G. W., Jamieson, R., & Lake, C. (2021). Biodegradation kinetics of individual and mixture non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in an agricultural soil receiving alkaline treated biosolids. Science of the Total Environment, 755, 142520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142520.
Trapp, S., & Eggen, T. (2013). Simulation of the plant uptake of organophosphates and other emerging pollutants for greenhouse experiments and field conditions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 4018-4029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1337-7
Van den Berg, P., Huerta-Lwanga, E., Corradini, F., & Geissen, V. (2020). Sewage sludge application as a vehicle for microplastics in eastern Spanish agricultural soils. Environmental Pollution, 261, 114198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114198
Vráblová, M., Smutná, K., Chamrádová, K., Vrábl, D., Koutník, I., Rusín, J., & Pavlíková, J. (2024). Co-composting of sewage sludge as an effective technology for the production of substrates with reduced content of pharmaceutical residues. Science of the Total Environment, 915, 169818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.169818
Wagener, S., Jungnickel, H., Dommershausen, N., Fischer, T., Laux, P., & Luch, A. (2019). Determination of nanoparticle uptake, distribution, and characterization in plant root tissue after realistic long-term exposure to sewage sludge using information from mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 5416–5426. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b07222.
Zhang, B., Zhou, X., Ren, X., Hu, X., & Ji, B. (2023). Recent research on municipal sludge as soil fertilizer in China: a review. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 234(2), 119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06142-w
Zhonghong, L., & Donghai Y. (2024). Global performance and trends of research on emerging contaminants in sewage sludge: A Bibliometric Analysis from 1990 to 2023. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 281, 116597, ISSN 0147-6513, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116597.