Contaminantes Emergentes Provenientes de Aplicación de Lodos Residuales en la Agricultura: Un análisis Bibliométrico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2220Palabras clave:
bioacumulación, biosólidos, indicadores bibliométricos, producción científica, VOSviewerResumen
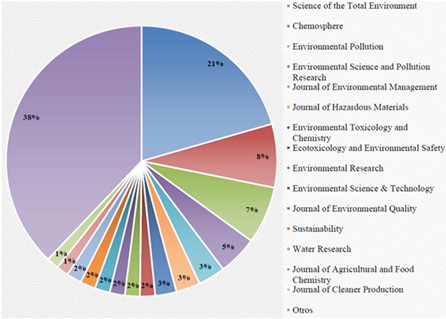
La producción de biosólidos en plantas tratadoras de aguas residuales representa un problema ambiental dado que aumenta paralelamente con la población. En la literatura se reportan artículos de investigación donde se aborda la aplicación de los lodos en la agricultura, surgiendo la preocupación del efecto de contaminantes emergentes (CE) que puedan estar contenidos en cultivos y el suelo. El objetivo del presente estudio fue analizar las tendencias de la producción científica en investigaciones relacionadas con la aplicación de los lodos residuales en la agricultura, en el periodo comprendido entre 1992 a 2024, mediante el uso de herramientas bibliométricas. Se realizó una búsqueda avanzada en Web of Science, específicamente en las bases de datos Science Citation Index Expanded y Social Science Citation Index, y se efectuó un análisis en Excel y VOSviewer de indicadores bibliométricos. Se obtuvieron 277 trabajos con registro publicados entre el período evaluado (1992-2024). La producción científica se ajustó a un crecimiento exponencial (R2=0.9124) lo que muestra un aumento de artículos publicados en estos años, del año 1922 a 2011 el incremento fue menor del 2%, posteriormente el crecimiento de las publicaciones fue mayor a 2% a diferencia del año 2021 donde el crecimiento fue mayor del 10%. El autor con el mayor número de trabajos publicados y registrados es Lapen D. R., mientras que el autor más citado es Huerta E. La revista con más artículos publicados es Science of the total Enviroment, siendo La Academia de Ciencias de China la institución con más trabajos con registro publicados y la de mayor interacción con instituciones de otros países. Se concluye que el crecimiento de publicaciones de artículos relacionados con la aplicación de lodos residuales a campos agrícolas y sus implicaciones concernientes a los CE, ha sido exponencial y que numerosos autores publican constantemente en este campo de estudio.
Descargas
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/D
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
Citas
Abril, C., Santos, J. L., Martín, J., Aparicio, I., & Alonso, E. (2021). Uptake and translocation of multiresidue industrial and household contaminants in radish grown under controlled conditions. Chemosphere, 268, 128823. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128823
Brown, S., Ippolito, J. A., Hundal, L. S., & Basta, N. T. (2020). Municipal biosolids—A resource for sustainable communities. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 14, 56-62. doi:10.1016/j.coesh.2020.02.007
Buta, M., Hubeny, J., Zieliński, W., Harnisz, M., & Korzeniewska, E. (2021). Sewage sludge in agriculture – the effects of selected chemical pollutants and emerging genetic resistance determinants on the quality of soil and crops – a review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 214, 112070. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112070
Clarke, B. O., & Smith, S. R. (2011). Review of 'emerging' organic contaminants in biosolids and assessment of international research priorities for the agricultural use of biosolids. Environment international, 37(1), 226–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2010.06.004
Clarke, B.O., Smith, S.R. (2018). Review of ‘emerging’ organic contaminants in biosolids and assessment of international research priorities for the agricultural use of biosolids. Environ. Int., 37, 226-247, 10.1016/j.envint.2010.06.004
Corradini, F., Meza, P., Eguiluz, R., Casado, F., Huerta-Lwanga, E., & Geissen, V. (2019). Evidence of Microplastic Accumulation in Agricultural Soils from Sewage Sludge Disposal. Sci. Total Environ., 671, 411– 420, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.368
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285-296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Fromme, H., Küchler, T., Otto, T., Pilz, K., Müller, J., & Wenzel, A. (2002). Occurrence of phthalates and bisphenol A and F in the environment. Water research, 36(6), 1429-1438. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00367-0
Gao, D., Li, X. Y., & Liu, H. T. (2020). Source, occurrence, migration and potential environmental risk of microplastics in sewage sludge and during sludge amendment to soil. Science of the Total Environment, 742, 140355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140355
Gubišová, M., Horník, M., Hrčková, K., Gubiš, J., Jakubcová, A., Hudcovicová, M., & Ondreičková, K. (2020). Sewage Sludge as a Soil Amendment for Growing Biomass Plant Arundo donax L. Agronomy, 10(5), 678. doi:10.3390/agronomy10050678
Jones V., Gardner M., & Ellor B. (2014). Concentrations of trace substances in sewage sludge from 28 wastewater treatment works in the UK Chemosphere, 111, 478-484
Hirsch, J. E. (2005). An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences, 102(46), 16569-16572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507655102
Lamastra, L., Suciu, N. A., & Trevisan, M. (2018). Sewage sludge for sustainable agriculture: contaminants’ contents and potential use as fertilizer. Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture, 5(1), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-018-0122-3
Li, J., Wang, Y., & Yan, B. (2018). The hotspots of life cycle assessment for bioenergy: A review by social network analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 625, 1301-1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.030
Li, Z., & Yuan, D. (2024). Global performance and trends of research on emerging contaminants in sewage sludge: A Bibliometric Analysis from 1990 to 2023. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 281, 116597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116597
Marchuk, S., Tait, S., Sinha, P., Harris, P., Antille, D. L., & McCabe, B. K. (2023). Biosolids-derived fertilisers: A review of challenges and opportunities. Science of the Total Environment, 875, 162555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162555
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & Prisma Group. (2010). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. International Journal of Surgery (london, England), 8(5), 336–341.
Niknejad, N., Ismail, W., Bahari M., Hendradi, R., & Salleh, A. Z. (2021) ‘Mapping the research trends on blockchain technology in food and agriculture industry: a bibliometric analysis’, Environ. Technol. Innovat., 21, doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2020.101272
Pérez-Lemus, N., López-Serna, R., Pérez-Elvira, S. I., & Barrado, E. (2019). Analytical methodologies for the determination of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in sewage sludge: A critical review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1083, 19-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.06.044
Pérez, R. A., Sánchez-Brunete, C., Albero, B., Miguel, E., Tadeo, J. L., Alonso, J., & Lobo, M. C. (2016). Quality assessment of three industry-derived organic amendments for agricultural use. Compost Science & Utilization, 24(3), 190-202. https://doi.org/10.1080/1065657X.2015.1124817
Sorinolu, A. J., Tyagi, N., Kumar, A., & Munir M. (2021). Antibiotic resistance development and human health risks during wastewater reuse and biosolids application in agriculture, Chemosphere, 265, 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129032
Seleiman, M. F., Santanen, A., & Mäkelä, P. S. (2020). Recycling sludge on cropland as fertilizer–Advantages and risks. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 155, 104647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104647
Shoaib, M., Zhang, S., & Ali, H. (2023). A bibliometric study on blockchain-based supply chain: a theme analysis, adopted methodologies, and future research agenda. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(6), 14029-14049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24844-2
Shu, W., Price, G. W., Jamieson, R., & Lake, C. (2021). Biodegradation kinetics of individual and mixture non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in an agricultural soil receiving alkaline treated biosolids. Science of the Total Environment, 755, 142520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142520.
Trapp, S., & Eggen, T. (2013). Simulation of the plant uptake of organophosphates and other emerging pollutants for greenhouse experiments and field conditions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 4018-4029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1337-7
Van den Berg, P., Huerta-Lwanga, E., Corradini, F., & Geissen, V. (2020). Sewage sludge application as a vehicle for microplastics in eastern Spanish agricultural soils. Environmental Pollution, 261, 114198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114198
Vráblová, M., Smutná, K., Chamrádová, K., Vrábl, D., Koutník, I., Rusín, J., & Pavlíková, J. (2024). Co-composting of sewage sludge as an effective technology for the production of substrates with reduced content of pharmaceutical residues. Science of the Total Environment, 915, 169818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.169818
Wagener, S., Jungnickel, H., Dommershausen, N., Fischer, T., Laux, P., & Luch, A. (2019). Determination of nanoparticle uptake, distribution, and characterization in plant root tissue after realistic long-term exposure to sewage sludge using information from mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 5416–5426. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b07222.
Zhang, B., Zhou, X., Ren, X., Hu, X., & Ji, B. (2023). Recent research on municipal sludge as soil fertilizer in China: a review. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 234(2), 119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06142-w
Zhonghong, L., & Donghai Y. (2024). Global performance and trends of research on emerging contaminants in sewage sludge: A Bibliometric Analysis from 1990 to 2023. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 281, 116597, ISSN 0147-6513, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116597.