Factores que Influyen en la Disposición a Pagar por el Compostaje Doméstico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2286Palabras clave:
economía, reciclaje, residuos sólidos urbanos, sustentabilidad, valoración contingenteResumen
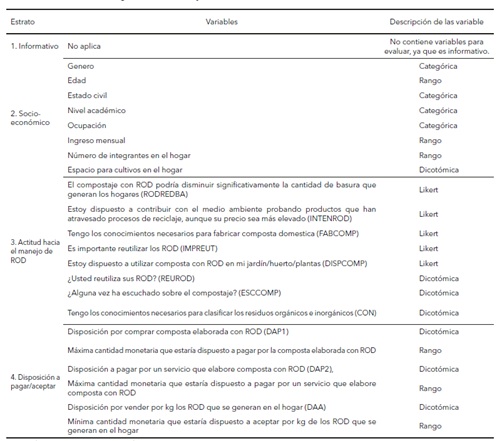
La gestión de los residuos orgánicos domésticos (ROD) representa un desafío persistente para la mayoría de los países en desarrollo, principalmente por la escasez de sitios para su revalorización. El compostaje doméstico es una técnica eficaz para gestionar los residuos orgánicos, ya que permite obtener un producto con valor agregado (la composta) y reducir el volumen total de los residuos sólidos urbanos. El objetivo de esta investigación fue identificar los factores que influyen en la disposición a pagar por el aprovechamiento de residuos orgánicos domésticos mediante el compostaje (1) la disposición por comprar composta elaborada con ROD, (2) la disposición a pagar por un servicio que elabore composta con ROD, y (3) la disposición a vender ROD por kg que se generan en el hogar. Se aplicó el método de valoración contingente con una muestra de 382 hogares de la ciudad de La Paz, Baja California Sur. Los factores se identificaron a través del modelo de regresión logística binaria. Los resultados indicaron que las variables que mostraron efecto fueron la ocupación, edad, número de integrantes en el hogar, estar de acuerdo a contribuir con el medio ambiente probando productos que han atravesado procesos de reciclaje, aunque su precio sea más elevado.
Descargas
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/D
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
Citas
Abdel-Shafy, H. I., & Mansour, M. S. M. (2018). Solid waste issue: Sources, composition, disposal, recycling, and valorization. Egyptian Journal of Petroleum, 27(4), 1275–1290. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpe.2018.07.003
Agbefe, L. E., Lawson, E. T., & Yirenya-Tawiah, D. (2019). Awareness on waste segregation at source and willingness to pay for collection service in selected markets in Ga West Municipality, Accra, Ghana. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 21(4), 905–914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00849-x
Atelge, M. R., Krisa, D., Kumar, G., Eskicioglu, C., Nguyen, D. D., Chang, S. W., Atabani, A. E., Al-Muhtaseb, A. H., & Unalan, S. (2020). Biogas production from organic waste: Recent progress and perspectives. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 11(3), 1019–1040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-00546-0
Atinkut, H. B., Yan, T., Arega, Y., & Raza, M. H. (2020). Farmers’ willingness-to-pay for eco-friendly agricultural waste management in Ethiopia: A contingent valuation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 261(121211). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121211
Ayilara, M., Olanrewaju, O., Babalola, O., & Odeyemi, O. (2020). Waste management through composting: Challenges and potentials. Sustainability, 12(11), 4456. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114456
Azqueta Oyarzun, Diego. (2007). Introducción a la economía ambiental. España. MCGRAW-HILL.
Benyam, A., Rolfe, J., & Kinnear, S. (2020). Willingness to pay for a domestic food waste diversion policy option in regional Queensland, Australia. Journal of Cleaner Production, 270(122485), 122485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122485
H. Congreso del Estado de Baja California Sur. (2022): Ley de manejo integral de residuos sólidos para B.C.S., Boletín No. 266. https://www.cbcs.gob.mx/index.php/boletines-2022-1/6258-propone-gabriela-montoya-ley-de-manejo-integral-de-residuos-solidos-para-bcs
Brotosusilo, A., Nabila, S., Negoro, H.A., & Utari, D. (2020). The level of individual participation of community in implementing effective solid waste management policies. Global Journal of Environmental Science and Management, 6, 341-354.
Ceballos Pérez SG &Flores Xolocotzi R. (2022). Una prueba de hipótesis de la curva ambiental de Kuznets para residuos sólidos urbanos en México, 1992-2018. Revista de Economía. 39(99). http://dx.doi.org/10.33937/reveco.2022.275
Chen, D. M.-C., Bodirsky, B. L., Krueger, T., Mishra, A., & Popp, A. (2020). The world’s growing municipal solid waste: trends and impacts. Environmental Research Letters, 15(7), pp. 074021. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/ab8659
Chen, T., Zhang, S., & Yuan, Z. (2020). Adoption of solid organic waste composting products: A critical review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 272(122712), 122712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122712
Dika, G., Nemie, A., & Birhane, E. (2019). Household’s willingness to pay for improved solid waste management in gulelle sub city, Addis Ababa. Energy and Environmental Engineering, 6(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.13189/eee.2019.060101
Dwinadine, Y. & Dewi, E. (2020). The Purpose of Intention to Use Composting for Waste Management in Bandung Area. Asian Journal of Research in Business and Management. 2(2), 197–206. https://myjms.mohe.gov.my/index.php/ajrbm/article/view/10326/4882
Fattah, M. A., Rimi, R. A., & Morshed, S. R. (2022). Knowledge, behavior, and drivers of residents’ willingness to pay for a sustainable solid waste collection and management system in Mymensingh City, Bangladesh. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 24(4), 1551–1564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-022-01422-9
Fávero, L. P., Belfiore, P., & de Freitas Souza, R. (2023). Binary and multinomial logistic regression models. Data Science, Analytics and Machine Learning with R. Elsevier Science.
Ferronato, N., & Torretta, V. (2019). Waste mismanagement in developing countries: A review of global issues. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,16(6), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061060
Ghazali, E. M., Nguyen, B., Mutum, D. S., & Yap, S.-F. (2019). Pro-environmental behaviours and Value-Belief-Norm theory: Assessing unobserved heterogeneity of two ethnic groups. Sustainability, 11(12), 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123237
Heidari, R., Yazdanparast, R., & Jabbarzadeh, A. (2019). Sustainable design of a municipal solid waste management system considering waste separators: A real-world application. Sustainable Cities and Society,47(101457),101457. doi 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101457
Hénault-Ethier, L., Martin, J.-P., & Housset, J. (2017). A dynamic model for organic waste management in Quebec (D-MOWIQ) as a tool to review environmental, societal and economic perspectives of a waste management policy. Waste Management, 66, 196–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.04.021
Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI) (2021). Censo Nacional de Gobiernos Municipales y Demarcaciones Territoriales de la Ciudad de México. Recuperado de https://www.inegi.org.mx/programas/cngmd/2021/
Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI), (2020). Demografía y sociedad, Vivienda. Recuperado de https://www.inegi.org.mx/programas/ccpv/2020/
Ke, J., Cai, K., Yuan, W., Li, J., & Song, Q. (2022). Promoting solid waste management and disposal through contingent valuation method: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 379(134696), 134696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134696
Knickmeyer, D. (2020). Social factors influencing household waste separation: A literature review on good practices to improve the recycling performance of urban areas. Journal of Cleaner Production, 245(118605), 118605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118605
Li, S., & Kallas, Z. (2021). Meta-analysis of consumers’ willingness to pay for sustainable food products. Appetite, 163(105239), 105239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2021.105239
Marcello, B., Di Gennaro, V., & Ferrini, S. (2021). Let the citizens speak: An empirical economic analysis of domestic organic waste for community composting in Tuscany. Journal of Cleaner Production, 306(127263), 127263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127263
Massoud, M., Lameh, G., Bardus, M., & Alameddine, I. (2021). Determinants of waste management practices and willingness to pay for improving waste services in a low-middle income country. Environmental Management, 68(2), 198–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-021-01472-z
Mutandwa, E., Grala, R. K., & Petrolia, D. R. (2019). Estimates of willingness to accept compensation to manage pine stands for ecosystem services. Forest Policy and Economics,102, 75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forpol.2019.03.001
McGurk, E., Hynes, S., & Thorne, F. (2020). Participation in agri-environmental schemes: A contingent valuation study of farmers in Ireland. Journal of Environmental Management, 262(110243), 110243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110243
Nguyen, T. T. T., Malek, L., Umberger, W. J., & O’Connor, P. J. (2022). Household food waste disposal behaviour is driven by perceived personal benefits, recycling habits and ability to compost. Journal of Cleaner Production, 379(134636), 134636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134636
Norton, E. C., Dowd, B. E., & Maciejewski, M. L. (2019). Marginal effects-quantifying the effect of changes in risk factors in logistic regression models. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association, 321(13), 1304–1305. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.1954
Quispe Mamani, J. C., Guevara Mamani, M., Marca Maquera, V. R., Mamani Sonco, V. Y. F., & Marca Maquera, H. R. (2020). Estimación de la disposición a pagar por un sistema de recolección mejorado de residuos sólidos domésticos en la ciudad de Juliaca 2020. Ciencia & Desarrollo,26, 77–87. https://doi.org/10.33326/26176033.2020.26.935
Sagaró del Campo, N. M., & Zamora Matamoros, L. (2019). Análisis estadístico implicativo versus Regresión logística binaria para el estudio de la causalidad en salud. Multimed,23(6), 1416–1440. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1028-48182019000601416
Saldaña D., & C. E., Nájera G., O. (2019). Identificación de sitios con potencial para la disposición final de residuos sólidos urbanos en el municipio de Tepic, Nayarit, México. Revista Internacional de Contaminación Ambiental, 35, 69–77. doi: 10.20937/rica.2019.35.esp02.07
Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (SEMARNAT) (2017). Recuperado de https://www.gob.mx/semarnat/acciones-y-programas/residuos-solidos-urbanos rsu#:~:text=Informaci%C3%B3n%20sobre%20residuos%20s%C3%B3lidos%20urbanos.&text=En%20M%C3%A9xico%20se%20generan%20diariamente,9.63%25%20de%20los%20residuos%20generados.
Sewak, A., Kim, J., Rundle-Thiele, S., & Deshpande, S. (2021). Influencing household-level waste-sorting and composting behaviour: What works? A systematic review (1995-2020) of waste management interventions”.Waste Management & Research: The Journal of the International Solid Wastes and Public Cleansing Association, ISWA,39(7), 892–909. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X20985608
Shah, A. V., Srivastava, V. K., Mohanty, S. S., & Varjani, S. (2021). Municipal solid waste as a sustainable resource for energy production: State-of-the-art review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(4), 105717. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105717
Sindhu, R., Gnansounou, E., Rebello, S., Binod, P., Varjani, S., Thakur, I. S., Nair, R. B., & Pandey, A. (2019). Conversion of food and kitchen waste to value-added products. Journal of Environmental Management, 241, 619–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.053
Spiegel, M. R., & Stephens, L. J. (2009). Estadística. Cuarta edición. México, D. F.: MCGRAW-HILL. ISBN-13: 978-970-10-6887-8.
Sulewski P, Kais K, Gołaś M, Rawa G, Urbańska K, Wąs A. (2021). Home bio-waste composting for the circular economy. Energies. 14(19):6164. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/en14196164
Tassie, K., & Endalew, B. (2020). Willingness to pay for improved solid waste management services and associated factors among urban households: One and one half bounded contingent valuation study in Bahir Dar city, Ethiopia. Cogent Environmental Science,6(1), 1807275. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311843.2020.1807275
Vigoroso, L., Pampuro, N., Bagagiolo, G., & Cavallo, E. (2021). Factors influencing adoption of compost made from organic fraction of municipal solid waste and purchasing pattern: A survey of Italian professional and hobbyist users. Agronomy, 11(6), 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061262
Wu, Z., Zhang, Y., Chen, Q., & Wang, H. (2021). Attitude of Chinese public towards municipal solid waste sorting policy: A text mining study. The Science of the Total Environment. 756(142674), 142674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142674
Wiyanti, S., & Erdi, M. S. (2023). The role green marketing and product knowledge in strengthening consumer purchasing decisions for compost fertilizer at Tegal District. Enrichment: Journal of Management. 13(3) https://www.enrichment.iocspublisher.org/index.php/enrichment/article/view/1533/1109
Yaashikaa, P. R., Kumar, P. S., Nhung, T. C., Hemavathy, R. V., Jawahar, M. J., Neshaanthini, J. P., & Rangasamy, G. (2022). A review on landfill system for municipal solid wastes: Insight into leachate, gas emissions, environmental and economic analysis. Chemosphere, 309, 136627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136627
Zand, A. D., Heir, A. V., & Tabrizi, A. M. (2020). Investigation of knowledge, attitude, and practice of Tehranian women apropos of reducing, reusing, recycling, and recovery of urban solid waste. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(7), 481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08445-5