Application of Bokashi and Mountain Microorganisms in Corn Cultivation in Chenalhó, Chiapas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2140Keywords:
biofertilizer, soil fertility, tornamilAbstract
Organic manures and microbial biofertilizers have been positioned as agroecological alternatives with potential to improve soil fertility and food production sustainability, whose use reduces dependence on external inputs and contributes to environmental health. The objective of the present work is to evaluate the effect of mountain microorganisms (MM) and Bokashi (B) organic manure on soil fertility, growth and yield of corn crop in tornamil sowing (Nov 2023-June 2024) in the community of Campo Los Toros, Chenalhó, Chiapas. Four treatments were evaluated: T1 (control), T2 (MM), T3 (Bokashi) and T4 (MM+Bokashi) with a randomized block design with five replications. The MM treatment consisted of a consortium of bacteria, fungi and actinomycetes prepared with the reproduction and activation techniques
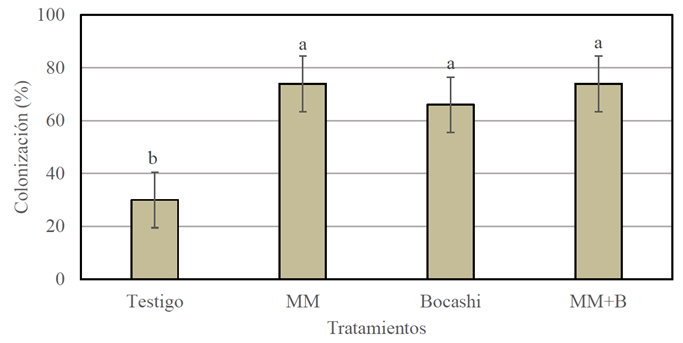
and applied diluted to 50% with water by spraying soil near the plant stem, with a dose of 3 L 120 m-2, every 15 days until 120 days after planting. Bokashi was made with organic materials available in the community and applied at planting with a dose of 500 g mata-1. The corn growth in height, stem diameter and number of leaves during the vegetative period did not show significant differences among treatments (P ≥ 0.05). The microbial C-biomass content was 172.8% higher with MM than the control (P ≤ 0.05). Available phosphorus (Olsen) and mycorrhizal colonization percentage were 153.0 and 126.7% higher with MM+B treatment than the control. Grain yield was 82.4% higher with Bokashi than in the other treatments. Therefore, Bokashi proved to be a promising agricultural practice with potential to increase corn grain yield.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.