Impact of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles as a Biostimulant in Strawberry Crop
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2198Keywords:
antioxidants, calcium phosphate, nanotechnology, phytochemical compoundsAbstract
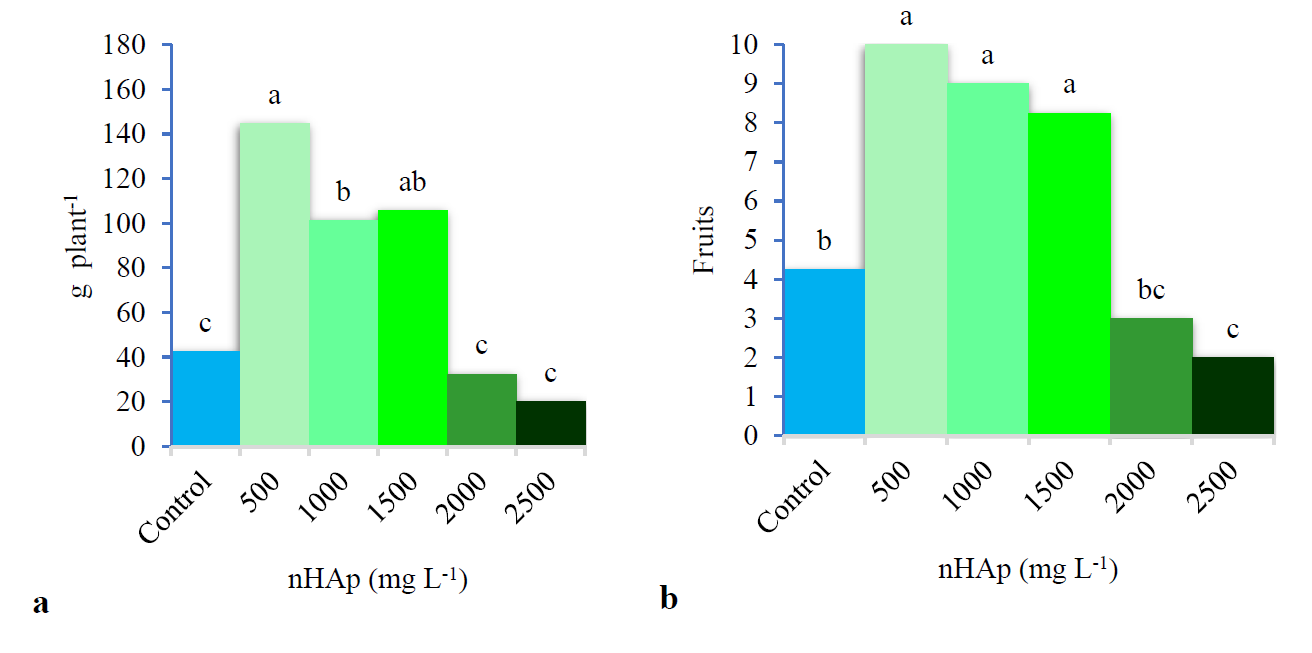
Biostimulation is the process by which plants respond and activate components of secondary metabolism, allowing the accumulation of biologically active substances in fruits and thereby improving their organoleptic and nutritional quality. In this research, the biostimulant ef fect of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (nHAp) on strawberry crops was evaluated. The treatments included foliar application of increasing doses of nHAp; 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, and 2500 mg L-1, and a control (deionized water). Foliar application of nHAp on strawberries significantly improved yield, commercial quality, and content of bioactive compounds in the fruit. The dose of 500 mg L-¹ showed the best yield and fruit firmness, while higher doses increased bioactive compounds, although with a decreasing trend in productivity. These results show the potential of nHAp as an agricultural biostimulant, highlighting the need to determine optimal doses specific to each crop.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.